This repository documents the implementation of three java interfaces ("node_info", "WGraph_DS", WGraph_Algo) that together define the second assignment in the Object Oriented Programing class at Ariel University.
The assignment was defined by the three interfaces mentioned in the previous section
and its goal was split into two parts.In the first part I had to build a weighted undirected graph data structure,
as defined by the node_info and WGraph_ds interfaces.
In the second part I had to build a class that would operate on a graph such as the one I
built in the first part of the assignment, as defined by the weighted_graph_algoritmns
interface.
In order to build a graph data structure, I used two primary hashmaps, as well as a
secondary third one (all details can be viewed in javadoc format in the WGraph_DS class
in lines 99 and 102). In order to define what a node in such a graph looks like I Implemented
the node_info interface as an inner class of WGraph_DS.
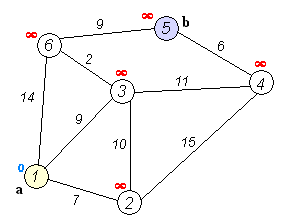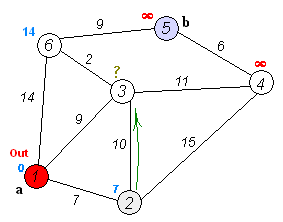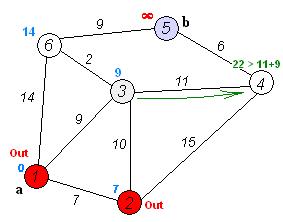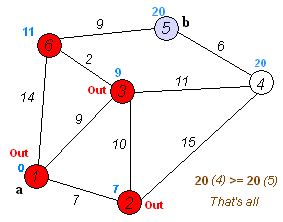
A big part of this assignment was to understand and implement Dijkstra's algorithm to find the shortest path between two nodes in the graph. I used the traditional implementation, using priority queue to monitor which part of the graph I should explore next. The algorithm's way of exploring the graph can be best explained by the following animation.
The Wgraph_Algo class is the one that runs Dijkstra's algorithm. In order to find the shortest path
one must first build a graph using the WGraph_Ds class and then initiate a WGraph_Algo
object that will point at your graph. (WGraph_Algo works with its own underlying graph).
After that, you can access the shortestPath or shortestPathDist methods through the WGraph_Algo
object you created.
Here's a code snippet of an exemplary main method that uses the algorithm:
public static void main(String[] args) {
weighted_graph graph = new WGraph_DS();//A graph data structure
weighted_graph_algorithms alg = new WGraph_Algo();//A graph algo object
graph.addNode(0);
graph.addNode(1);
graph.addNode(2);
graph.addNode(3);
graph.addNode(4);
graph.connect(0,1,2);
graph.connect(2,1,1);
graph.connect(4,1,6);
graph.connect(2,3,2);
graph.connect(3,4,1);
alg.init(graph);//alg will now apply all its algorithms with graph
List<node_info> path = alg.shortestPath(0,4);//This list will hold the shortest path from 0 to 4
}