-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 99
BatchSpecific
Tri Nguyen-Huu edited this page May 6, 2022
·
19 revisions
When an experiment of type Batch is run, a dedicated UI is displayed, depending on the parameters to explore and of the exploration methods.
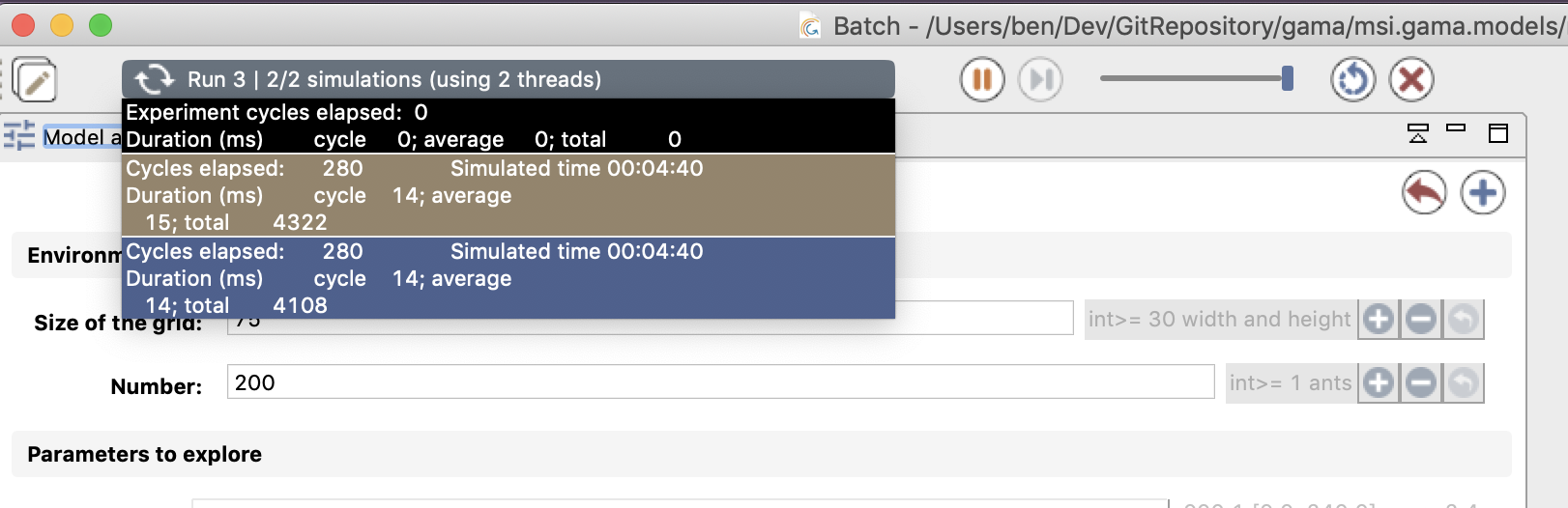
In batch mode, the top information bar displays 3 distinct information (instead of only the cycle number in the GUI experiment):
- The run number: One run corresponds to N executions of simulation with one given parameters values (N is an integer given by the facet
repeatin the definition of a batchexperiment. The number of runs is chosen by the exploration method). - The simulation number: the number of replications done (and the number of replications specified with the
repeatfacet); - The number of thread: the number of threads used for the simulation.
The parameters view is also a bit different in the case of a Batch UI:
- it shows both the parameters of the experiment, with a distinction between the ones that will be explored and the ones that will not.
- it also shows the state of the exploration. The provided information will depend on the exploration method.
The following interface is generated given the following experiment (the exploration method is here the exhaustive one):
experiment Batch type: batch repeat: 2 keep_seed: true until: (food_gathered = food_placed) or (time > 400) {
parameter 'Size of the grid:' var: gridsize init: 75 unit: 'width and height';
parameter 'Number:' var: ants_number init: 200 unit: 'ants';
parameter 'Evaporation:' var: evaporation_per_cycle among: [0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 0.8, 1.0] unit: 'rate every cycle (1.0 means 100%)';
parameter 'Diffusion:' var: diffusion_rate min: 0.1 max: 1.0 unit: 'rate every cycle (1.0 means 100%)' step: 0.3;
method exhaustive maximize: food_gathered;
}
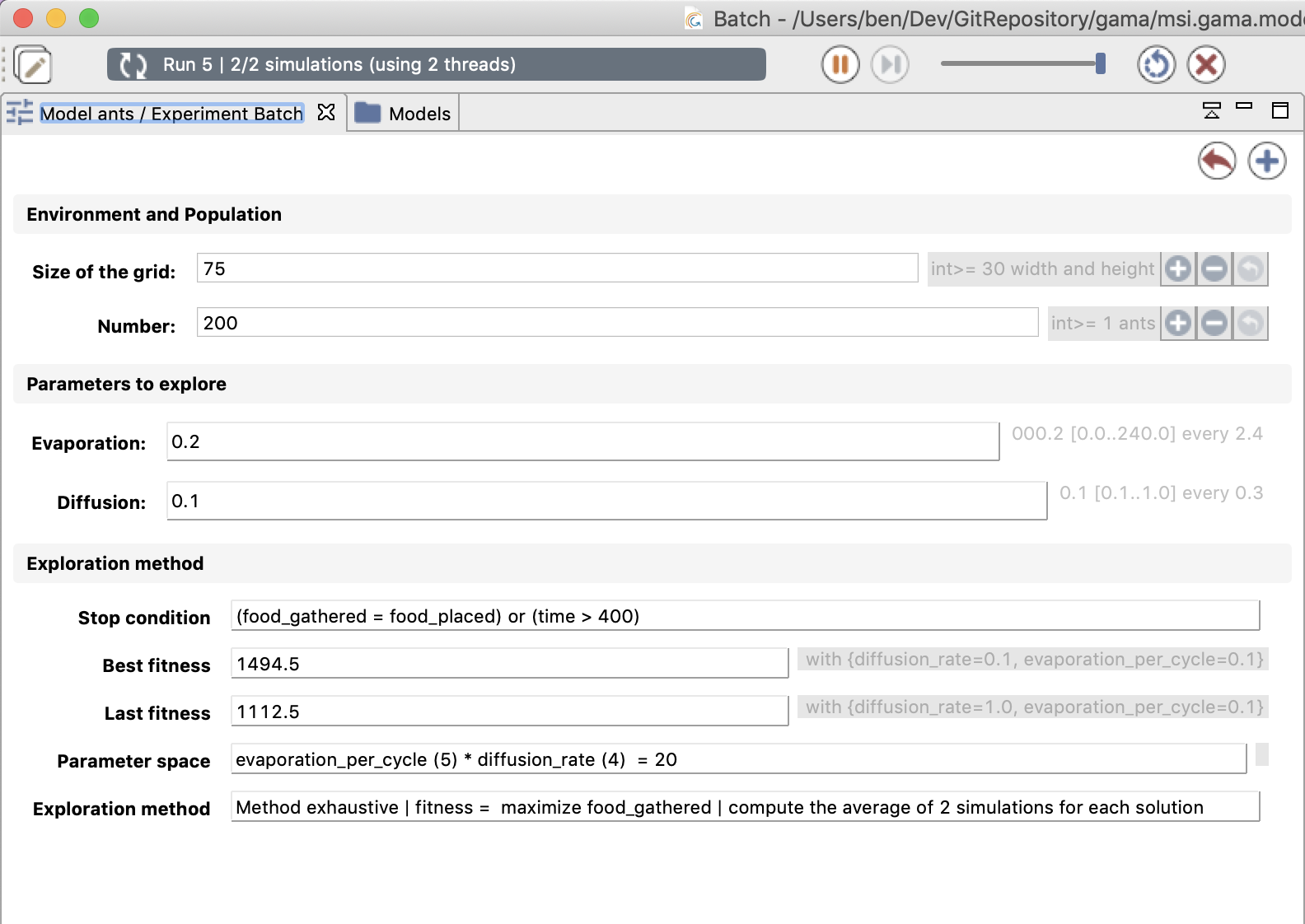
The interface summarises all model parameters and the parameters given to the exploration method:
-
Environment and Population: displays all the model parameters that should not be explored. Those parameters must be initialized with a fixed value when they are defined in the
experiment. -
Parameters to explore: the parameters to explore are the parameters defined in the experiment with a range of values (with
amongfacet ormin,maxandstepfacets); - Exploration method: it displays information about the exploration method and the stop condition. It displays the size of the parameter space in the case of the exhaustive method, and different parameters (e.g. mutation or crossover probability...) for other methods. Finally, the best and the last fitnesses found are shown, along with the associated parameter sets.
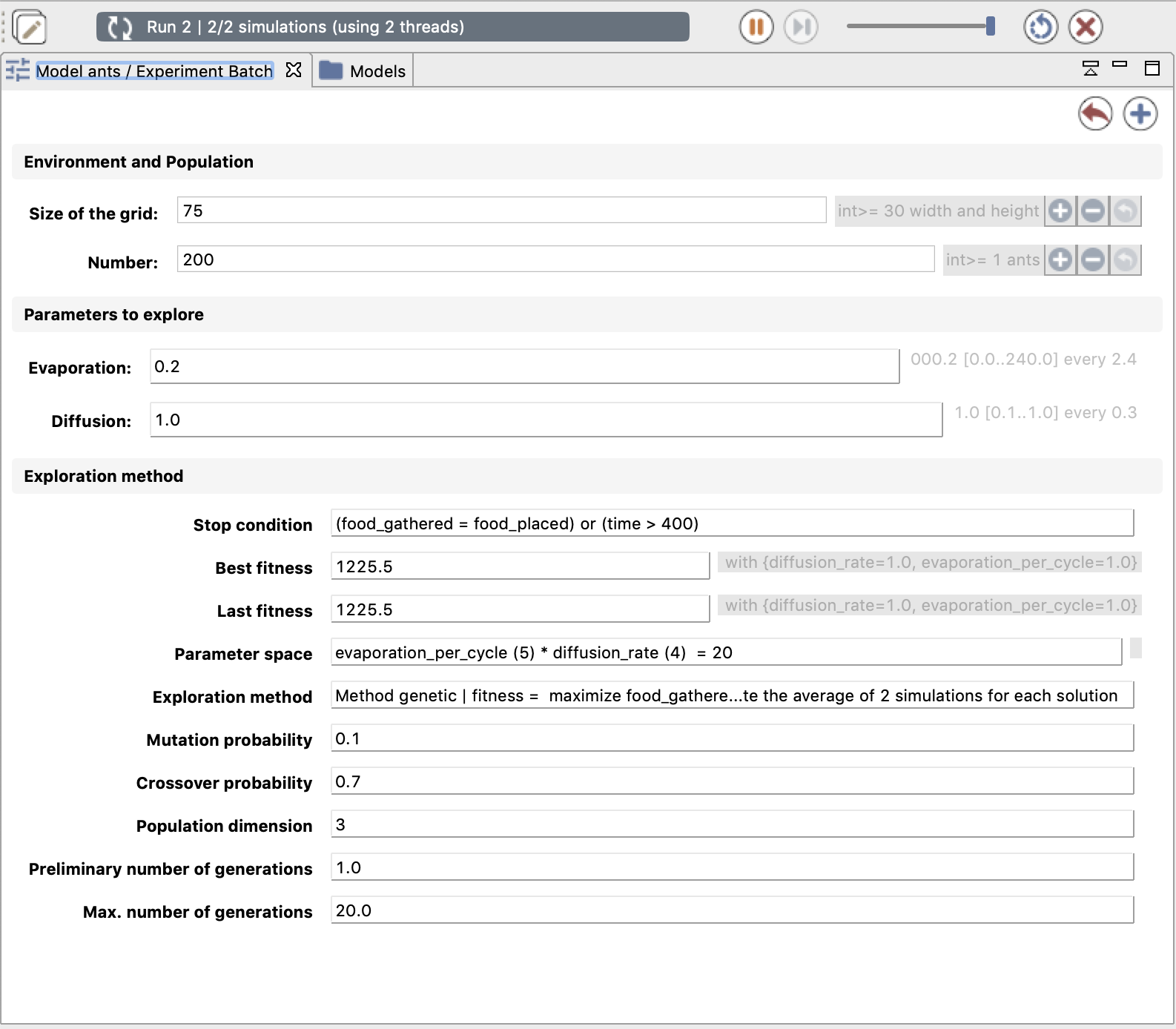
The following interface corresponds to the same experiment as previously, but with the genetic exploration method.
experiment Batch type: batch repeat: 2 keep_seed: true until: (food_gathered = food_placed) or (time > 400) {
// [Parameters]
method genetic maximize: food_gathered;
}
- Installation and Launching
- Workspace, Projects and Models
- Editing Models
- Running Experiments
- Running Headless
- Preferences
- Troubleshooting
- Introduction
- Manipulate basic Species
- Global Species
- Defining Advanced Species
- Defining GUI Experiment
- Exploring Models
- Optimizing Model Section
- Multi-Paradigm Modeling
- Manipulate OSM Data
- Diffusion
- Using Database
- Using FIPA ACL
- Using BDI with BEN
- Using Driving Skill
- Manipulate dates
- Manipulate lights
- Using comodel
- Save and restore Simulations
- Using network
- Headless mode
- Using Headless
- Writing Unit Tests
- Ensure model's reproducibility
- Going further with extensions
- Built-in Species
- Built-in Skills
- Built-in Architecture
- Statements
- Data Type
- File Type
- Expressions
- Exhaustive list of GAMA Keywords
- Installing the GIT version
- Developing Extensions
- Introduction to GAMA Java API
- Using GAMA flags
- Creating a release of GAMA
- Documentation generation