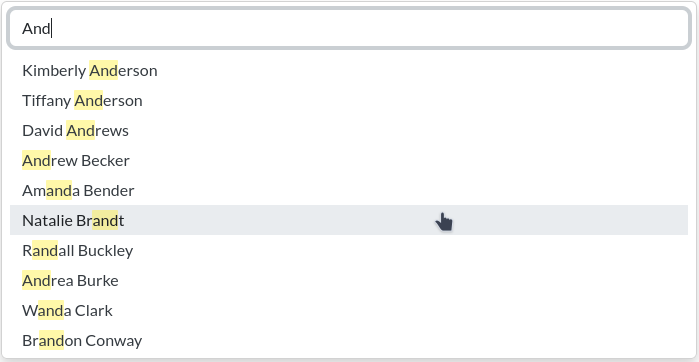
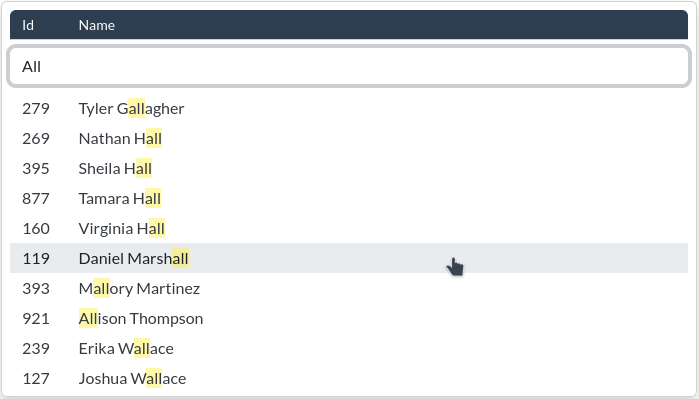
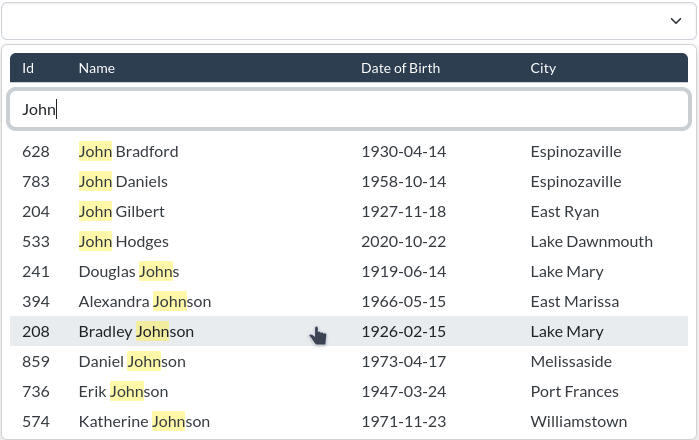
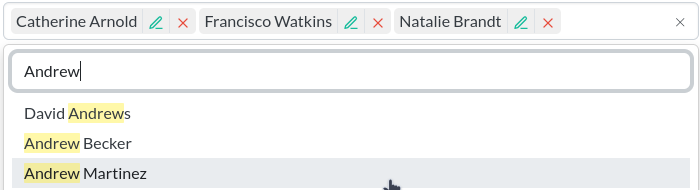
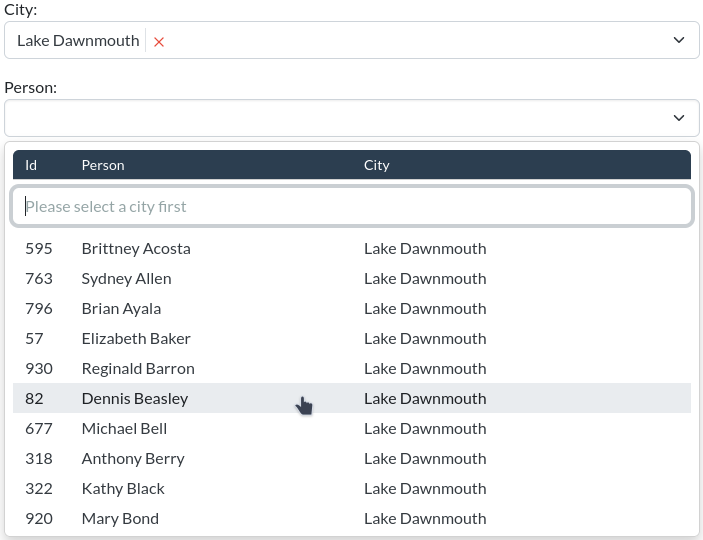
Django autocomplete widgets and views using TomSelect.
Note that this was written specifically with the MIZDB app in mind - it may not apply to your app.
Install:
pip install -U mizdb-tomselectAdd to installed apps:
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
"mizdb_tomselect"
]Configure an endpoint for autocomplete requests:
# urls.py
from django.urls import path
from mizdb_tomselect.views import AutocompleteView
urlpatterns = [
...
path('autocomplete/', AutocompleteView.as_view(), name='my_autocomplete_view')
]Use the widgets in a form.
from django import forms
from mizdb_tomselect.widgets import MIZSelect, MIZSelectTabular
from .models import City, Person
class MyForm(forms.Form):
city = forms.ModelChoiceField(
City.objects.all(),
widget=MIZSelect(City, url='my_autocomplete_view'),
)
# Display results in a table, with additional columns for fields
# 'first_name' and 'last_name':
person = forms.ModelChoiceField(
Person.objects.all(),
widget=MIZSelectTabular(
Person,
url='my_autocomplete_view',
search_lookup="full_name__icontains",
# for extra columns pass a mapping of model field: column header label
extra_columns={'first_name': "First Name", "last_name": "Last Name"},
# The column header label for the labelField column
label_field_label='Full Name',
),
)NOTE: Make sure to include bootstrap somewhere. For example in the template:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>MIZDB TomSelect Demo</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"
integrity="sha384-kenU1KFdBIe4zVF0s0G1M5b4hcpxyD9F7jL+jjXkk+Q2h455rYXK/7HAuoJl+0I4"
crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet"
integrity="sha384-rbsA2VBKQhggwzxH7pPCaAqO46MgnOM80zW1RWuH61DGLwZJEdK2Kadq2F9CUG65" crossorigin="anonymous">
{{ form.media }}
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<form>
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_div }}
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-success">Save</button>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>The widgets pass attributes necessary to make autocomplete requests to the HTML element via the dataset property. The TomSelect element is then initialized from the attributes in the dataset property.
Base autocomplete widget. The arguments of MIZSelect are:
| Argument | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| model | required | the model class that provides the choices |
| url | "autocomplete" |
view name of the autocomplete view |
| value_field | f"{model._meta.pk.name}" |
model field that provides the value of an option |
| label_field | getattr(model, "name_field", "name") |
model field that provides the label of an option |
| search_lookup | f"{label_field}__icontains" |
the lookup to use when filtering the results |
| create_field | model field to create new objects with (see below) | |
| changelist_url | view name of the changelist view for this model (see below) | |
| add_url | view name of the add view for this model(see below) | |
| edit_url | view name of the edit view for this model(see below) | |
| filter_by | a 2-tuple defining an additional filter (see below) | |
| can_remove | True | whether to display a remove button next to each item |
This widget displays the results in tabular form. A table header will be added to the dropdown. By default, the table contains two columns: one column for the choice value (commonly the "ID" of the option) and one column for the choice label (the human-readable part of the choice).
MIZSelectTabular has the following additional arguments:
| Argument | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| extra_columns | a mapping for additional columns | |
| value_field_label | f"{value_field.title()}" |
table header for the value column |
| label_field_label | f"{model._meta.verbose_name}" |
table header for the label column |
To add more columns, pass a result attribute name: column label mapping to the widget
argument extra_columns. For example:
# models.py
class Person(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=100, blank=True)
dob = models.DateField(blank=True, null=True)
city = models.ForeignKey("City", on_delete=models.SET_NULL, blank=True, null=True)
# forms.py
class TabularForm(forms.Form):
person = forms.ModelChoiceField(
Person.objects.all(),
widget=MIZSelectTabular(
Person,
extra_columns={"dob": "Date of Birth", "city__name": "City"},
label_field_label="Name",
),
required=False,
)The column label is the table header label for a given column (here: Date of Birth and City).
The attribute name tells TomSelect what value to look up on a result for the column (here: model field dob and lookup
expression city__name on the relation field city).
Important: that means that the result visible to TomSelect must have an attribute
or property with that name or the column will remain empty.
The results for TomSelect are created by the view calling values() on the
result queryset, so you must make sure that the attribute name is available
on the view's root queryset as either a model field or as an annotation.
Variants of the above widgets that allow selecting multiple options.
The AutocompleteView filters the result queryset against the search_lookup
passed to the widget. The default value for the lookup is name__icontains.
Overwrite the AutocompleteView.search method to modify the search process.
class MyAutocompleteView(AutocompleteView):
def search(self, request, queryset, q):
# Filter using your own queryset method:
return queryset.search(q)To enable option creation in the dropdown, pass the view name of the add view for the given model to the widget. This will add an 'Add' button to the bottom of the dropdown.
# urls.py
urlpatterns = [
...
path('autocomplete/', AutocompleteView.as_view(), name='my_autocomplete_view'),
path('city/add/', CityCreateView.as_view(), name='city_add'),
]
# forms.py
widget = MIZSelect(City, url='my_autocomplete_view', add_url='city_add')Clicking on that button sends the user to the add page of the model.
NOTE: Also see Add & Edit popup response
If create_field was also passed to the widget, clicking on the button will
create a new object using an AJAX POST request to the autocomplete URL. The
autocomplete view will use the search term that the user put in on the
create_field to create the object:
class AutocompleteView:
def create_object(self, data):
"""Create a new object with the given data."""
return self.model.objects.create(**{self.create_field: data[self.create_field]})Override the view's create_object method to change the creation process.
The dropdown will include a link to the changelist of the given model if you pass in the view name for the changelist view.
# urls.py
urlpatterns = [
...
path('autocomplete/', AutocompleteView.as_view(), name='my_autocomplete_view'),
path('city/change/', CityChangelistView.as_view(), name='city_changelist'),
]
# forms.py
widget = MIZSelect(City, url='my_autocomplete_view', changelist_url='city_changelist')Provide a edit_url to attach a link to the edit/change page for each selected item.
# urls.py
urlpatterns = [
...
path('person/edit/<path:object_id>/', PersonChangeView.as_view(), name='person_change'),
]
# forms.py
widget = MIZSelect(Person, edit_url='person_change')NOTE: Also see Add & Edit popup response
Use the filter_by argument to restrict the available options to the value of
another field. The parameter must be a 2-tuple: (name_of_the_other_form_field, django_field_lookup)
# models.py
class Person(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
pob = models.ForeignKey("Place of Birth", on_delete=models.SET_NULL, blank=True, null=True)
class City(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
# forms.py
class PersonCityForm(forms.Form):
city = forms.ModelChoiceField(queryset=City.objects.filter(is_capitol=True))
person = forms.ModelChoiceField(
queryset=Person.objects.all(),
widget=MIZSelect(
Person,
filter_by=("city", "pob_id")
)
)This will result in the Person result queryset to be filtered against
pob_id with the current value of the city formfield.
NOTE: When using filter_by, the declaring element now requires that the other field
provides a value. If the other field does not have a value, the search will not
return any results.
After adding new objects with the 'add' button or after editing selected objects with the
'edit' button, the options of the 'parent' form will still need to be updated.
This can be done by using the PopupResponseMixin view mixin with your CreateViews and UpdateViews.
from mizdb_tomselect.views import PopupResponseMixin
class CityCreateView(PopupResponseMixin, CreateView):
...
class PersonChangeView(PopupResponseMixin, UpdateView):
...You also need to modify the template for the Create-/UpdateView by adding a hidden field to the form:
<form>
...
{% if is_popup %}
<input type="hidden" name="{{ is_popup_var }}" value="1">
{% endif %}
...
</form>With all this in place, tabs opened from (left-)clicking an add or edit button will be
treated as a popup. When submitting a popup form, the view redirects to a popup response
template. That template loads some javascript that updates the form of the opener window
that created the popup. The popup window or tab is then closed.
This is, roughly, a slimmed down version of how django admin handles popups for related objects.
To change MIZSelect or TomSelect settings, you can add a handler for the initMIZSelect event.
The event is dispatched before the TomSelect constructor is called.
The target of the event is the element that is about to be initialized.
You can pass your own settings to the init function initMIZSelect that is attached to the target element.
For example, to overwrite the title of the remove buttons:
window.addEventListener('initMIZSelect', (e) => {
const elem = e.target
const mySettings = { plugins: { remove_button: { title: 'Remove This' } } }
elem.initMIZSelect(mySettings)
})The settings will be merged with the default MIZSelect settings, and the TomSelect constructor will be called with the merged settings.
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
make initSee the demo for a preview: run make init-demo and then start the demo server python demo/manage.py runserver.
Run tests with make test or make tox. To install required browsers for playwright: playwright install.
See the makefile for other commands.