forked from qinwf/re2r
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
/
README.rmd
186 lines (132 loc) · 4.52 KB
/
README.rmd
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
---
title: "README.rmd"
output:
md_document:
variant: markdown_github
---
```{r setup, include=FALSE}
knitr::opts_chunk$set(echo = TRUE)
library(re2r)
```
# re2r
[](https://travis-ci.org/qinwf/re2r) [](https://ci.appveyor.com/project/qinwf/re2r/branch/master) [](http://cran.r-project.org/package=re2r) [](https://codecov.io/gh/qinwf/re2r)
RE2 is a primarily DFA based regexp engine from Google that is very fast at matching large amounts of text.
## Installation
From CRAN:
```r
install.packages("re2r")
```
From GitHub:
```r
library(devtools)
install_github("qinwf/re2r", build_vignettes = T)
```
To learn how to use, you can check out the [vignettes](https://qinwenfeng.com/re2r_doc/).
## Related Work
[Google Summer of Code](https://github.com/rstats-gsoc/gsoc2016/wiki/re2-regular-expressions) - re2 regular expressions.
## Brief Intro
### 1. Search a string for a pattern
`re2_detect(string, pattern)` searches the string expression for a pattern and returns boolean result.
```{r}
test_string = "this is just one test";
re2_detect(test_string, "(o.e)")
```
Here is an example of email pattern.
```r
show_regex("\\b[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\\.[a-zA-Z]{2,4}\\b", width = 670, height = 280)
```
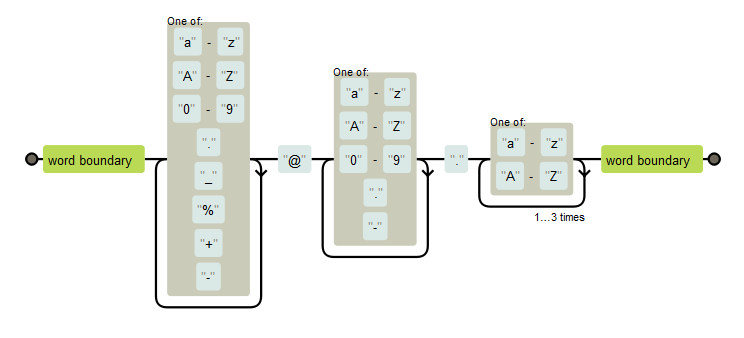
```{r}
re2_detect("[email protected]", "\\b[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\\.[a-zA-Z]{2,4}\\b")
```
`re2_match(string, pattern)` will return the capture groups in `()`.
```{r}
(res = re2_match(test_string, "(o.e)"))
```
The return result is a character matrix. `.1` is the first capture group and it is unnamed group.
Create named capture group with `(?P<name>pattern)` syntax.
```{r}
(res = re2_match(test_string, "(?P<testname>this)( is)"))
is.matrix(res)
is.character(res)
res$testname
```
If there is no capture group, the matched origin strings will be returned.
```{r}
test_string = c("this is just one test", "the second test");
(res = re2_match(test_string, "is"))
```
`re2_match_all()` will return the all of patterns in a string instead of just the first one.
```{r}
res = re2_match_all(c("this is test",
"this is test, and this is not test",
"they are tests"),
pattern = "(?P<testname>this)( is)")
print(res)
is.list(res)
```
match all numbers
```{r}
texts = c("pi is 3.14529..",
"-15.34 °F",
"128 days",
"1.9e10",
"123,340.00$",
"only texts")
(number_pattern = re2(".*?(?P<number>-?\\d+(,\\d+)*(\\.\\d+(e\\d+)?)?).*?"))
(res = re2_match(texts, number_pattern))
res$number
```
```r
show_regex(number_pattern)
```
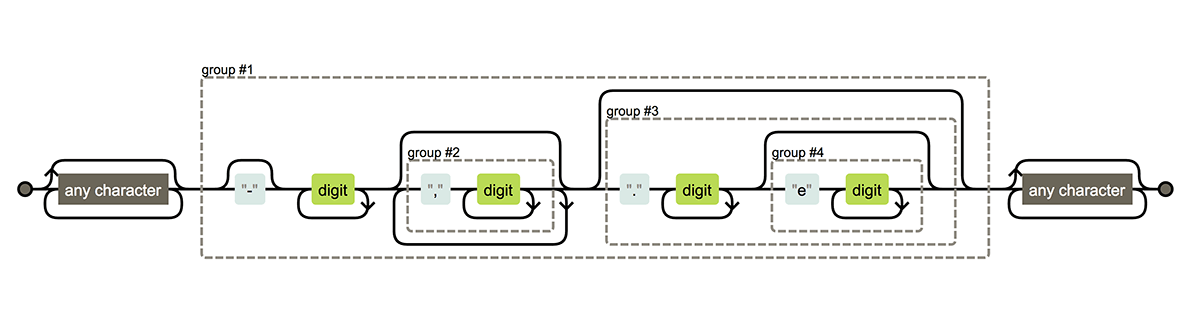
### 2. Replace a substring
```r
re2_replace(string, pattern, rewrite)
```
Searches the string "input string" for the occurence(s) of a substring that matches 'pattern' and replaces the found substrings with "rewrite text".
```{r}
input_string = "this is just one test";
new_string = "my"
re2_replace(new_string, "(o.e)", input_string)
```
mask the middle three digits of a US phone number
```{r}
texts = c("415-555-1234",
"650-555-2345",
"(416)555-3456",
"202 555 4567",
"4035555678",
"1 416 555 9292")
us_phone_pattern = re2("(1?[\\s-]?\\(?\\d{3}\\)?[\\s-]?)(\\d{3})([\\s-]?\\d{4})")
re2_replace(texts, us_phone_pattern, "\\1***\\3")
```
### 3. Extract a substring
```r
re2_extract(string, pattern, replacement)
```
Extract matching patterns from a string.
```{r}
re2_extract("yabba dabba doo", "(.)")
```
```{r}
re2_extract("[email protected]", "(.*)@([^.]*)")
```
### 4. `Regular Expression Object` for better performance
We can create a regular expression object (RE2 object) from a string. It will reduce the time to parse the syntax of the same pattern.
And this will also give us more option for the pattern. run `help(re2)` to get more detials.
```{r}
regexp = re2("test",case_sensitive = FALSE)
print(regexp)
```
```{r}
regexp = re2("test",case_sensitive = FALSE)
re2_match("TEST", regexp)
re2_replace("TEST", regexp, "ops")
```
### 5. Multithread
Use `parallel` option to enable multithread feature. It will improve performance for large inputs with a multi core CPU.
```r
re2_match(string, pattern, parallel = T)
```