| layout | title | nav_order | permalink |
|---|---|---|---|
default |
Gallery |
6 |
/gallery |
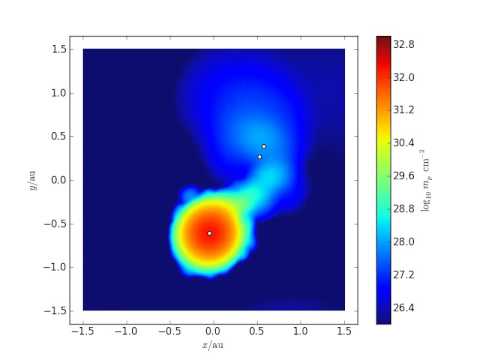
Evolution of the triple star system Xi Tau in the constellation Taurus. The tertiary (outer) giant star overflows its Roche lobe at pericenter. We simulate the system using the AMUSE framework (see amusecode.org), using a combination of stellar evolution, gravitational dynamics and hydrodynamics. Reference to the scientific paper: 2014MNRAS.438.1909D. The script to simulate the evolution of this system can be downloaded from: http://www.amusecode.org/doc/examples/.
Simulation of a star cluster starting from clumpy initial conditions. Includes the effect of mass loss from the stellar evolution. Simulated using AMUSE. Rendered as you would see it with the Hubble Space Telescope, if it would snap a picture every 31250 year, that is!
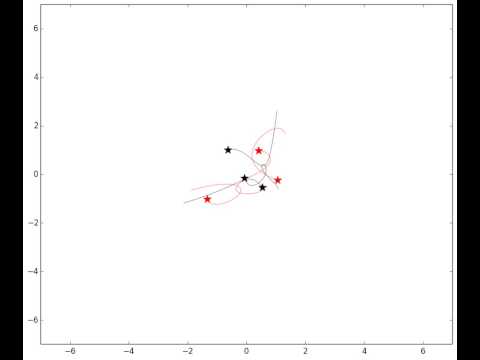
Evolution of the Pythagorean triple system of 3 objects with relative
masses 3, 4 and 5, positioned on the corners of a triangle with
coordinates (1, 3), (-2, -1) and (1, -1) in the
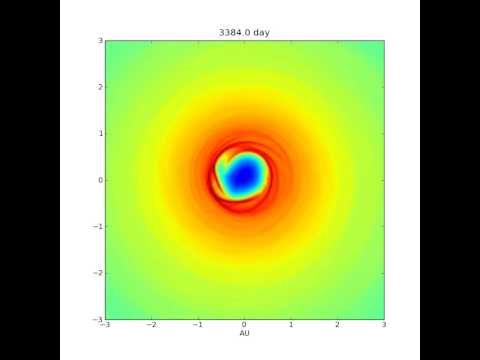
Evolution of a proto-planetary disk around Kepler 16. Movie shows the evolution of a disk with a mass 0.01 solar masses around a binary system with stars of 0.7 and 0.2 solar mass. The simulations show that the location of density enhancement at the inner rim matches the current orbits of Kepler 16 and similar systems, published in 2013MNRAS.429..895P.
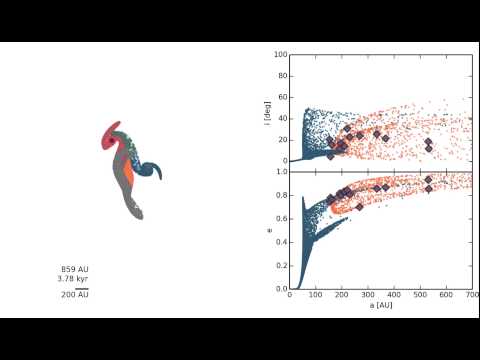
Animation of the encounter between the Sun (blue) and Q (red) both with planetesimal disks. The Sun captures the Sednito's whereas Q captures some of the Sun's Kuiper belt objects. Unbound objects turn gray. The orbital elements (semi-major axis, eccentricity and inclination) are presented in the right panels. The diamonds give the known Sednitos.
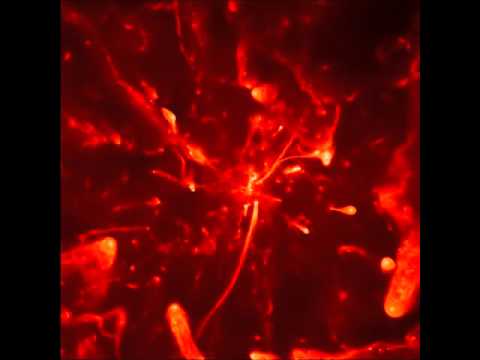
Simulate the windy S-stars in orbit around the Galactic center (see 2016MNRAS.456.3645L)
Animation of the S-stars in orbit around the supermassive black hole in the Galactic center (in the middle of the animation). The winds of the stars are turned on at the start of the movie, and develope a chaotic multi wind-shock region around the black hole, which accretes from the frothy wind. You can also follow individual stars, such as for example S-66, S-67 and S-72:
Below are links to some of the nice work other groups are doing with AMUSE:
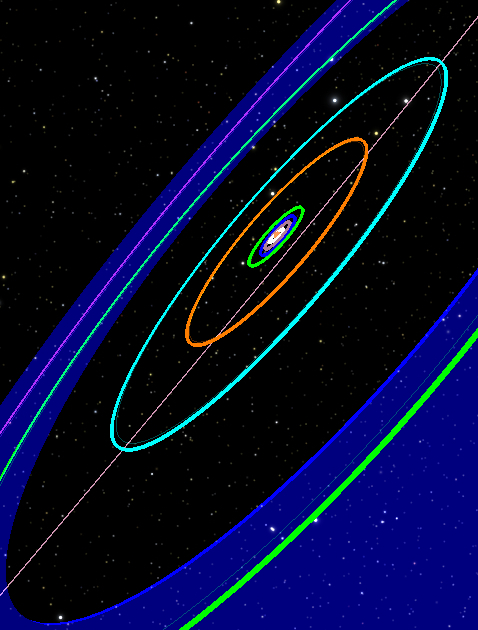
A simulation of the Late Evolution of Our Solar System by Aaron Geller